
[ad_1]
Some of the stunning issues to come back out of the primary half of 2022 was the walloping fastened earnings buyers acquired from bonds. The Bloomberg U.S. Combination Bond Index posted its worst 12-month return in its complete historical past, which prompted many buyers to shed exposures, notably longer-term sectors.
Now that the mud has settled a bit, speaking to buyers about reconsidering the area could be very a lot an uphill battle. I get it. Inflation continues to rise, additional charge hikes are on the horizon, and up to date returns are the worst in many years. That doesn’t current a really enticing state of affairs for a hard and fast earnings investor. However let’s take a look at the place issues are prone to go versus the place they’ve been.
Inflation and Charges
It’s laborious to have a dialog about fastened earnings with out speaking about inflation, so let’s begin there. As I discussed in a earlier publish, there’s sturdy proof to counsel that inflation has peaked. Except for meals and vitality, the core parts of inflation look like rolling over, as proven within the chart beneath. Most of the areas that led inflation greater all through the pandemic (e.g., used automobiles and vans, dwelling furnishing, and housing) at the moment are beginning to see worth moderation as inventories construct and demand slows.
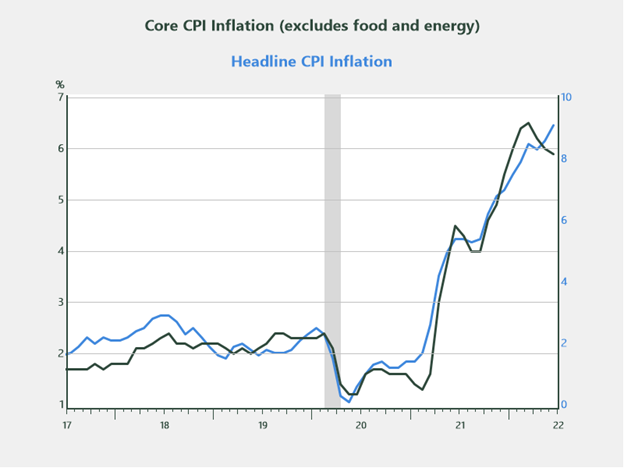
Supply: Haver Analytics
Core inflation represents about 80 % of headline CPI. If present developments proceed, which they need to, the core part of CPI may have a dampening impact on the general inflation image as we transfer into the autumn months. This notion is at present being mirrored in markets, as evidenced by latest developments within the 10-year Treasury yield.
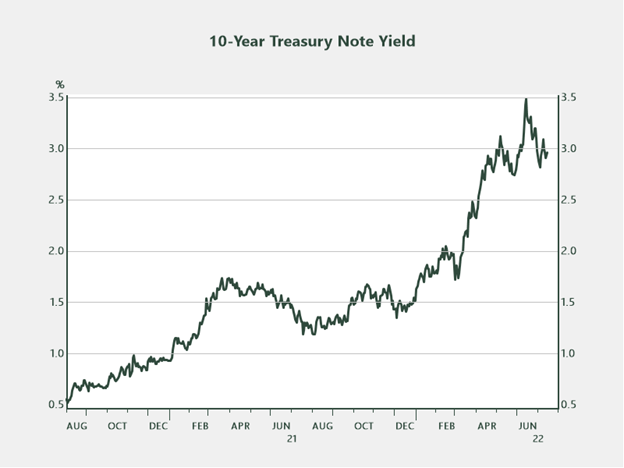
Supply: Haver Analytics
The second quarter of 2022 noticed the most important year-over-year inflation numbers in 40 years, but the 10-year Treasury yield is buying and selling across the identical degree it was when the quarter began. This reality means that buyers consider inflation is transitory versus structural and that the financial system could also be inching towards a slowdown—a state of affairs that’s being mirrored within the form of the yield curve as of late.
Yield Curve
The yield curve displays investor sentiment because it pertains to short- and long-term projections of the financial system and charges. Presently, buyers are promoting U.S. short-term Treasuries in anticipation of additional charge hikes from the Fed. Brief-term yields are transferring greater, whereas longer-term charges are repricing decrease in anticipation of moderating inflation and an financial contraction. The result’s what’s known as a curve inversion, a state of affairs that has pre-dated each recession (the grey areas within the chart) over the previous 40 years by roughly 12–18 months. If this historic relationship holds, it will arrange a recessionary state of affairs in some unspecified time in the future in mid-to-late 2023.
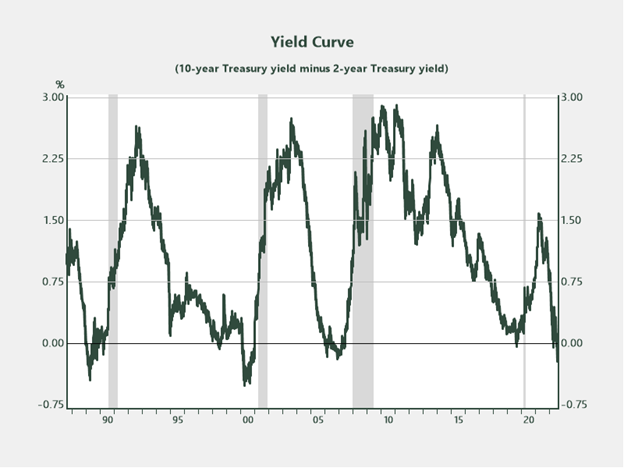
Supply: Haver Analytics
Mounted Earnings Outlook
Larger-quality, longer-maturity sectors. Contemplating the potential of an financial slowdown on the horizon (mixed with moderating inflation), the prospects for high-quality fastened earnings look good, notably longer-maturity investment-grade segments. When the financial system slows and the Fed is pressured to react by decreasing short-term charges, buyers typically search out higher-yielding, longer-maturity areas. Costs in these sectors are likely to rise as demand outpaces provide.
Decrease-quality segments. One space that succumbed to a substantial quantity of promoting strain within the first half of 2022 is the high-yield area. Presently, the yield-to-worst on the Bloomberg U.S. Company Excessive Yield Index is 8.7 %, a degree that’s solely been reached 3 times up to now decade. The worth of bonds within the index is averaging $87 (par of $100), which isn’t too far off from the place issues ended up within the 2020 downturn. As buyers think about their fastened earnings outlook and allocations, that is one space that deserves some consideration.
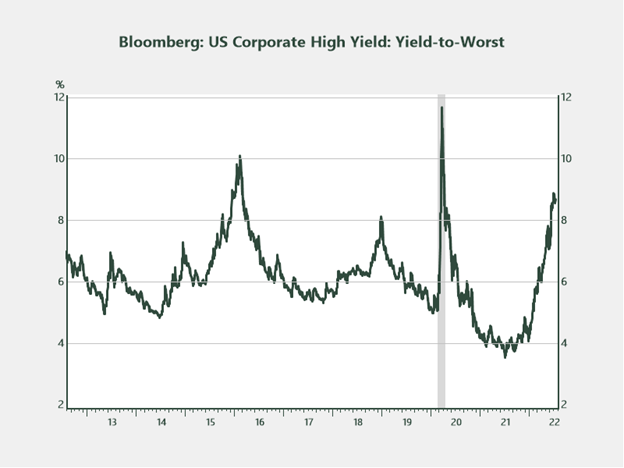
Supply: Haver Analytics
Municipal bonds. Just like different fastened earnings sectors, municipal bonds got here beneath loads of strain within the first half of the 12 months. The yield-to-worst on the BBB-rated BofA Merrill Lynch Municipal Index at present stands at 3.8 %, which equates to a 5.4 % taxable-equivalent yield for somebody within the 30 % tax bracket. Within the lower-credit-quality, high-yield municipal area, yields look much more enticing, with the Bloomberg Municipal Customized Excessive Yield Composite Index yielding 4.2 % (taxable equal of 6 %).
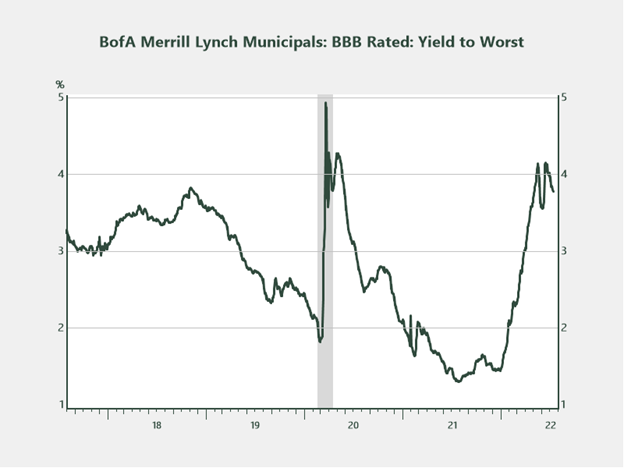
Supply: Haver Analytics
The Street Forward
Over the subsequent few quarters because the Fed continues with its aggressive method to curb inflation and markets digest each financial launch with fervor, there’s little question fastened earnings will expertise bouts of heightened volatility, as will equities. It’s by these durations of perceived chaos, nevertheless, that strategic long-term buyers ought to benefit from areas which were unduly offered. Durations when irrationality and emotion dominate markets usually current the most effective shopping for alternatives, and it now appears like a type of durations in fastened earnings.
Editor’s Be aware: The authentic model of this text appeared on the Unbiased Market Observer.
Municipal bonds are federally tax-free however could also be topic to state and native taxes, and curiosity earnings could also be topic to federal various minimal tax (AMT). Bonds are topic to availability and market situations; some have name options that will have an effect on earnings. Bond costs and yields are inversely associated: when the worth goes up, the yield goes down, and vice versa. Market danger is a consideration if offered or redeemed previous to maturity.
Excessive-yield/junk bonds make investments considerably in lower-rated bonds and are issued by corporations with out lengthy monitor data of gross sales and earnings or by these with questionable credit score power. Hostile adjustments within the financial system or poor efficiency by the issuers of those bonds could have an effect on the flexibility to pay principal and curiosity. Excessive-yield bonds contain substantial dangers, are typically extra risky, and is probably not appropriate for all buyers.
[ad_2]